Resultados de la búsqueda para: 894650K070
SENSOR, OXYGEN
Número de parte: 894650K070
Disponibilidad: 17
Peso, kg: 0.17
Order now:
Marca: Toyota
Made in: Indonesia

SENSOR, OXYGEN
Número de parte: 894650K070
Disponibilidad: 26
Peso, kg: 0.17
Procesando: 2-3 días
Marca: Toyota
Made in: Indonesia

Substituciones
SENSOR SUB-ASSY, HEIGHT CONTROL, REAR LH
Número de parte: 8940860020
Disponibilidad: 10
Peso, kg: 0.6
Order now:
Marca: Toyota
Made in: Japan

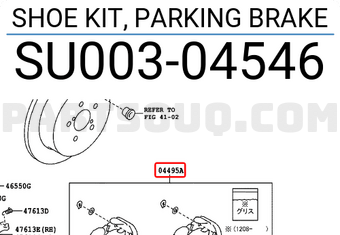
SHOE KIT, PARKING BRAKE
Número de parte: SU00304546
Disponibilidad: 10
Peso, kg: 1.873
Order now:
Marca: Toyota

SENSOR SUB-ASSY, HEIGHT CONTROL, REAR LH
Número de parte: 8940860020
Disponibilidad: 23
Peso, kg: 0.6
Procesando: 2-3 días
Marca: Toyota
Made in: Japan

SHOE KIT, PARKING BRAKE
Número de parte: SU00304546
Disponibilidad: 10
Peso, kg: 1.873
Procesando: 2-3 días
Marca: Toyota

Understanding the Oxygen Sensor for Vehicle Efficiency
The oxygen sensor is a crucial component in your vehicle's emission control system. It's responsible for measuring the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases being emitted from the engine. This data is sent to the engine control unit (ECU) to ensure a precise air-fuel mixture for optimal combustion efficiency. A perfect blend leads to increased fuel economy and reduced emissions, benefiting both your vehicle and the environment ?.
Why is the Oxygen Sensor Necessary?
The main purpose of this sensor is to maintain the right balance between air and fuel, which is vital for engine performance. Without it, the vehicle's ECU would not be able to adjust the air-fuel ratio, resulting in poor engine performance, increased emissions, and higher fuel consumption. This component plays a pivotal role in achieving compliance with environmental regulations and improving overall vehicle efficiency.
Functionality of the Oxygen Sensor
The oxygen sensor performs by detecting the concentration of oxygen in the exhaust. It generates a voltage signal based on the differential in oxygen content inside and outside the exhaust system. The ECU interprets this signal and makes necessary adjustments to the fuel injection system to maintain a stoichiometric air-fuel ratio, optimizing combustion.
Consequences of a Malfunctioning Sensor
If the oxygen sensor becomes faulty, it can lead to several engine problems. The ECU may receive incorrect data, causing either a rich or lean fuel mixture. Symptoms of a broken sensor include rough idling, misfires, poor acceleration, and increased fuel consumption ?. Ignoring these signs may result in expensive repairs and excessive emissions, failing emission tests.
- Fortuner
- Hilux